Gut Health

Gut health is the balance and functionality of the gastrointestinal tract, which includes the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The gut is essential to preserving overall health, given that it is involved in digestion, nutrient absorption.
Here are some important elements of gut health.
1. Microbiome:
The gut is home to a variety of bacteria, which are collectively referred to as the gut microbiome. Some examples of these microbes are bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes. For the maintenance of a healthy gut the balance of these microorganisms is important.

2. Absorption of nutrients:
A healthy gut helps break down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and used by the body for energy and other biological activities. A digestion and absorption of nutrients is essential for overall health.

3. Immune system:
The first line of defense against pathogens that enter the body through the digestive tract, the gut plays an important role in the immune system. A strong immune system and prevention of infection are both benefits of a healthy gut.
Gut Health Symptoms:
When your gut health is compromised, you might experience a variety of symptoms.
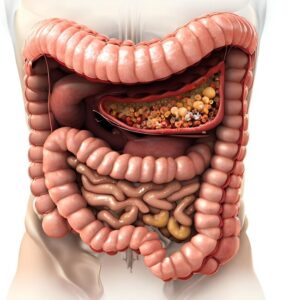
1. Digestive Problems :
Bloating: Feeling of fullness and tightness in the abdomen due to formation of gas. Feeling of gas formation or excessive belching. • Diarrhea: Constipation that is often watery or loose. Symptoms of constipation include difficulty passing stools, irregular bowel movements, or straining when going to the toilet. Abdominal cramps, discomfort or pain.

2. Food sensitivities or intolerances:
• Lactose intolerance: Problems with lactose digestion resulting in symptoms such as gas, bloating and diarrhea after consuming dairy products.
• Gluten sensitivity: An adverse reaction to foods containing gluten can result in symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain and altered bowel patterns.
3. Acid reflux and heartburn:
• Gastroesophageal reflux disease : Chronic acid reflux causes symptoms such as vomiting, heartburn and chest discomfort.
![]()
4. Unexplained weight change:
• Unintentional weight loss: Losing weight without intentionally changing your diet or exercise regimen may indicate a gastrointestinal condition.
• Weight gain: Some gut imbalances can cause weight gain or make it more difficult to lose weight.

5. Fatigue and low energy:
• Energy levels can be affected by gut health. Nutritional deficiencies due to poor gut health can lead to fatigue.

6. Skin conditions:
An imbalance in gut health can be responsible for conditions such as acne, eczema or psoriasis
some supplements often associated with gut health:

1. Probiotics:
Probiotics are live microorganisms that have a positive effect on health when consumed in adequate amounts. They may help to re-establish or maintain a balanced population of gut bacteria. Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi and other foods contain probiotics as well as supplements.

2. Prebiotics:
Prebiotics are dietary fibers that feed the good bacteria in your gut. They are present in foods such as onions, garlic, leeks, bananas and asparagus. Some supplements also contain prebiotic fibers.

3. Fiber Supplement:
Adequate amount of fiber is required for a healthy gut. In addition to encouraging regular bowel movements, fiber nourishes the good bacteria in the gut. Examples of supplemental fibers include psyllium husk, acacia fiber and inulin.

4. Digestive Enzymes:
These dietary supplements help in the digestion of specific nutrients. They can be helpful for people with specific digestive problems, but generally not everyone will need them.

5. L-Glutamine:
This amino acid is believed to help the lining of the gut stay healthy and repair itself. It is used by people suffering from diseases that affect the lining of the gut, such as leaky gut syndrome.

6. Fish Oil/Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil and other sources have anti-inflammatory properties and may support a healthy gut. These can be used as supplements or are present in fatty seafood such as salmon.

7. Collagen:
By increasing the integrity of the lining of the gut, collagen supplements are believed to enhance gut health. But there isn’t much evidence to support it.

8. Herbal Supplements:
Licorice root, slippery elm and aloe-vera are some of the plants that are believed to have a soothing effect on the gut and can be used to aid gut health.
The following should be considered when thinking about gut health supplements:

• Seek professional advice: Always check with your doctor before adding new supplements to your regimen, especially if you have ongoing medical problems or are using prescription drugs.

• Research:
Look for dietary supplements whose claims are backed by academicresearch. Informational resources include the Office of Dietary Supplements at the National Institutes of Health and accredited medical journals.

Dosage:
Follow dosage recommendations listed on supplement packaging.
Variety Diet Variety and balance are the cornerstones of a healthy gut. Emphasize eating whole foods that are high in fiber, minerals, and natural probiotics.